Ebase Security Authorization
Maintaining security roles and
authorizations
Rules for evaluating security
authorizations
Security Administration
Authorizations
Additional runtime authorizations
See
also: Ebase Startup Parameters
The Ebase
system is shipped with a built-in system for handling security authorization
that handles both designer and runtime security. This is activated by the
following line in UFSSetup.properties:
Ufs.authorisationManager=com.ebasetech.ufs.security.authorisation.EbaseAuthorisationManager
This system
can be replaced with an alternative authorization manager configured to connect
to an external security repository. This document describes the supplied Ebase
Authorization Manager.
Authorization
fundamentals
Each user
is associated with one or more security roles, where each role can
contain any number of individual authorizations. The association between
a user and their related roles is made when the user signs on – this may be to
the Ebase Designer or to the runtime environment. Each authorization controls
access to a specific resource, though masking characters (*) can be used.
Maintaining security roles and authorizations
The
security roles maintenance dialog is accessed from the tools menu (Tools
-> Maintain security) then clicking the Roles tab. This function
is only available to users with the following authorization:
|
Type |
SECADMIN |
|
Name |
ROLE |
|
Function |
Write |
Note that
function Read grants read-only access.
From this
dialog you can choose to maintain an existing role by double-clicking on a role
or clicking the Maintain Role button, delete an existing role, or create a new role.

Double-clicking on a role presents a dialog where authorizations for the role can be maintained.
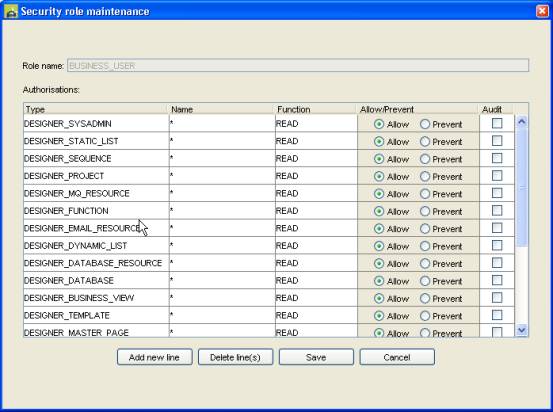
Authorizations
can be added or deleted using the Add new line and Delete line(s)
buttons.
Each
authorization consists of:
Type is
intended to be the generic name for a resource e.g. type DESIGNER_PROJECT
controls access to all Ebase Designer projects. Clicking in this field will
display a dropdown list of types supported by the Ebase Designer. However, a
type can also be entered by typing in the edit field. Values are case
sensitive.
Name
is intended to be a subset within type e.g. type DESIGNER_PROJECT, name
MY_PROJECT creates an authorization specific to a single project within the
Ebase Designer. Values are case sensitive.
Function
represents an explicit action e.g. Read, Write etc. Clicking in this field will
display a dropdown list of functions supported by the Ebase Designer. However,
a function can also be entered by typing in the edit field. Values are case
sensitive.
Allow/Prevent
determines whether the request should be allowed or prevented.
Audit:
clicking this checkbox indicates that when this authorization is used to
determine access, a log record is created. (See Auditing security
accesses).
The
dropdown checkboxes at the top of the dialog are used to include dropdown lists
for the Type and Function fields which are applicable for the Designer,
Runtime, and Workflow components respectively (see below).
Type, Name
and Function can contain a single * acting as a masking character e.g. the
authorization:
|
Type |
DESIGNER_* |
|
Name |
P* |
|
Function |
* |
|
Allow |
|
grants full access (i.e. all functions) to all designer
elements beginning with P.
The
authorization:
|
Type |
* |
|
Name |
* |
|
Function |
* |
|
Allow |
* |
grants full access to the entire system.
Rules for evaluating
security authorizations
The following
rules are used to determine whether a user has access to any given resource:
1.
If more than one authorization applies, the most
specific is used. The term most specific is interpreted as meaning the
highest number of characters that preceed any masking
character (*). e.g. ABCD* is more specific than AB*
which in turn is more specific than *. A value with no masking characters is always the most specific, and a
single masking character * is always the least specific. This logic is applied
first to the authorization type, then name, then
function to determine which of any two applicable authorizations should
be applied.
2.
If the authorization type, name
and function are all equal for any two authorizations being compared, an
authorization specifying prevent takes
precedence over an authorization specifying allow.
3.
If no authorization applies, the request is
denied.
4.
Some functions are implied by other functions as
follows:
|
Function |
Implies |
|
Read |
View, Export |
|
Write |
Read , View, Export, Import |
Ebase
Designer Authorizations
The
following authorization grants access to the Ebase Designer. Without this
authorization, a user will not be able to sign on to the Ebase Designer.
|
Type |
DESIGNER |
|
Name |
LOGON |
|
Function |
Read |
The
following table describes the additional authorizations used by the Ebase
Designer to control access to the various different design elements. Please
note that function CREATE is used to allow both creation and deletion of
elements.
|
Type |
Name |
Supported Functions |
Description |
|
DESIGNER_BATCH_ADMINISTRATION |
Batch name |
Read, Write, Create |
Used by the Ebase Batch system to display and administer batches: Read indicates read only Write grants full access Create grants the ability to delete batches |
|
DESIGNER_BATCH_EXECUTION |
Batch name |
Read |
Used by the Ebase Batch system to execute: Read indicates execute permission Write grants full administration access |
|
DESIGNER_BUSINESS_VIEW |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to business views Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_CUSTOM_RESOURCE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to custom resources Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_DATABASE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to database elements Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_DATABASE_RESOURCE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to database resources Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_DYNAMIC_LIST |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to dynamic lists Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_EMAIL_RESOURCE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to email resources Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER__FUNCTION |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to FPL function definitions Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_MASTER_PAGE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to print master pages Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_MQ_RESOURCE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to MQ resources Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_PRINTING_RESOURCE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to print resources Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_PROJECT |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to business projects and includes the ability to access all elements within a project Read indicates read only Write grants update access and includes the ability to create and delete forms and scripts within a project Create grants the ability to create and delete projects |
|
DESIGNER_SCHEDULER_ADMINISTRATION |
Element name |
Read, Write |
Controls access to the Ebase Scheduler Read indicates read access to scheduled tasks Write grants update access to scheduled tasks |
|
DESIGNER_SEQUENCE |
ALL or * |
Read, Write |
Controls access to all sequences Read indicates read only Write grants update access and the ability to create and delete sequences. Individual sequences cannot be protected. |
|
DESIGNER_STATIC_LIST |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to static lists Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_STORED_PROCEDURE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to stored procedure resources Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_SYSADMIN |
Element name |
Read, Write |
Controls access to the following dialogs under Tools: System Administration, System Texts Editor, System Preferences Read indicates read only Write grants full access |
|
DESIGNER_TEMPLATE |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to presentation templates Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_WEB_SERVICE |
ALL or * |
Read, Write |
Controls access to all web services definitions (Tools > Integration Server > Web Services) Read indicates read only including the ability to generate WSDL files. Write grants update access and the ability to create and delete web services. Individual web services cannot be protected. |
|
DESIGNER_WF_INTERACTIVE_ACTIVITY |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to workflow interactive activities Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_WF_PROCESS |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to workflow processes Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
|
DESIGNER_WF_SYSTEM_ACTIVITY |
Element name |
Read, Write, Create |
Controls access to workflow system activities Read indicates read only Write grants update access Create grants the ability to create and delete elements |
Security Administration
Authorizations
The following authorization is used to grant access to the
security administration dialogs:
|
Type |
Name |
Supported Functions |
Description |
|
SECADMIN |
ROLE |
Read, Write |
Grants access to the Role tab of the Security Administration dialog: Read indicates read only Write grants full access |
|
|
USER |
Read, Write |
Grants access to the Users and Groups tabs of the Security Administration dialog: Read indicates read only Write grants full access |
|
|
ENCRYPTION |
Read, Write |
Grants access to the Encryption tab of the Security Administration dialog: Read indicates read only Write grants full access |
Ebase Runtime
Authorizations
Form execution
authorization
The Ebase
runtime environment contains a single built-in authorization check which is
used to determine whether a user is authorised to run a form. This
authorization has the format:
Authorization:
|
Type |
Form |
|
Name |
See below |
|
Function |
Execute |
where Name is the value supplied in the Security
authorization field of the form properties
dialog for a form. In the following example, the authorization name is HIGH:
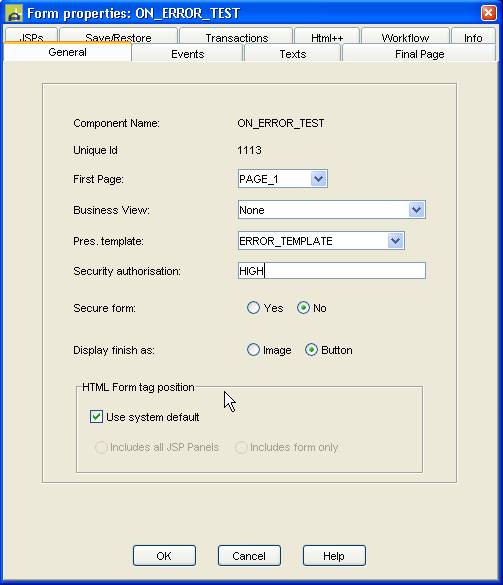
and access to this form (and all other forms with the same
security authorization name) could be controlled with an authorization such as
shown below:
Authorization:
|
Type |
Form |
|
Name |
HIGH |
|
Function |
Execute |
|
Prevent |
|
In this
example, access is denied.
If no
security authorization name is specified, all users are granted access to the
form.
If a
security authorization name is specified and an authenticated userid does not
exist, access is denied.
In all other
circumstances, the security system is checked to determine whether or not a
user has the required authorization.
When access
is denied, form execution is aborted. If a form on error event is not specified, this
results in the display of the system abort page with message:
********************************************
* Access denied to run form XXXXX *
********************************************
If an on
error event is specified, it receives control and system variable
$ABORT_MESSAGE is set with the message displayed above.
Additional runtime authorizations
Ebase forms
can check additional security authorizations using the FPL isAuthorized()
function. For example, the following example could be used to control access to
accounts:
Authorization:
|
Type |
Account |
|
Name |
Secure |
|
Function |
* |
|
Allow |
|
Script code:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
if [!isAuthorized('Account',
ACCOUNT_SECURITY_TYPE, 'Update' ) ] message 'Access denied'; endif |
if (!system.securityManager.isAuthorized( "Account",
fields.ACCOUNT_SECURITY_TYPE.value, "Update" ) ) { event.owner.addErrorMessage("Access
denied"); } |
Please note
that * cannot be used as a masking character for any of the arguments within
the isAuthorized() function.
Auditing security access
Each security authorization contains an audit
checkbox (See Maintaining security roles
and authorizations). When this is checked, an audit record is written to
the security log detailing the userid, the request ,
the authorization that was used to process the request, and whether the request
was allowed or denied. The security log files are controlled by the following
three parameters in UFSSetup.properties:
Ufs.auditLogDirName
Ufs.auditLogFileName
Ufs.retainOldAuditLogs
(See Ebase Startup Parameters for more information)
Please note that auditing all security requests will
generate a large volume of log data. It is recommended that audit logging is
only used to protect sensitive resources.
Ebase
Workflow Authorizations
All calls
to the workflow API are secured using a Type of WORKFLOW. In addition to
this, API calls that return a table of information e.g. getTasks,
getJobs etc include additional checks that each item
is viewable by the caller.
The Name part of the security authorization is taken from the security expression for the task or job to which the API call applies as shown in the following diagram. For task related commands, the security expression from the process will be used if no value is specified at task level. API calls that are not specific to a task or job e.g. getTasks() use the name CLIENT.
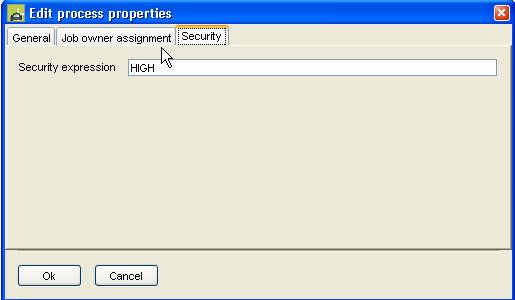
.
For
example, the following rule could be used to grant access to high security
(security expression = HIGH) workflow elements:
|
Type |
WORKFLOW |
|
Name |
HIGH |
|
Function |
* |
|
Allow |
|
The
following table shows the complete list of security authorizations checked by
the Ebase Workflow System.
|
Type |
Name |
Supported Functions |
Description |
|
WORKFLOW |
CLIENT |
getTasksForActor |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
getFailedTasks |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
getTasksForRole |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
assign |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
openTask |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
descriptorFor |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
unassign |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
setWaiting |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
pause |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
unpause |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
cancel |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
setPriority |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
reexecute |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
open1 |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
openJobAndCompleteFirstTask1 |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
getProcessInParameters |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
openedJobs |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
getAuditRecords |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
getJobs |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
getJobsForOwner |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
getTasks |
|
|
|
CLIENT |
getProcesses |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
cancelJob |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
complete |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
stateOf |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
descriptionOf |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
getCandidateActors |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
setOutputParameter |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
getProcessAttributeValue |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
setProcessAttributeValue |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
getProcessDescription |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
activateProcess |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
quiesceProcess |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
unsetJobOwner |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
forceCompletion |
|
|
|
Security Expression |
forceAssign |
|
|
WORKFLOW |
Security Expression |
VIEW |
Used to control visibility of individual line items within API calls that return a table of information e.g. getTasks, getJobs etc. |
Note 1:
Workflow functions open and openJobAndCompleteFirstTask
are always allowed for all users when using the provided security manager
EbaseSecurityManager.