Internationalization Support
Adding
and maintaining supported languages
Determining
User Runtime Language
How
texts are selected for display
Formatting
of numeric and date fields
Ebase
Designer Language Preference
†
See also:†††††† How to use Static Lists
Ebase provides full support for multiple languages,
the concept being that a form can be created once, and then run in any number
of languages.†
Any number of languages can be added to the Ebase
system as a supported language. When
a new user connects to the system, one of these supported languages is chosen
and set for the duration of their web session. This language is then used for
two purposes:
∑
To
display language sensitive text elements within the Ebase system Ė this
includes all texts (both form and system texts), static lists and messages.
∑
To
control the formatting of numeric and date fields when data is presented to the
user or entered by the user.
Adding and maintaining
supported languages
The system is supplied with the following supported
languages: Dutch, English, French, German, Polish, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish
and Welsh. Additional languages can be added and existing supported languages
can be modified using the Languages
tab of the internationalization dialog on the tools menu (Tools -> System
Preferences -> Internationalization)
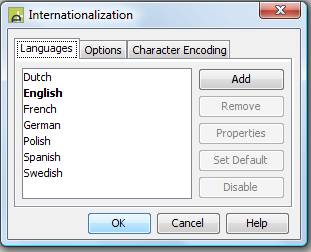
The list on the left shows all supported languages
defined to the system.
Add - add a
new language to the system.†
Remove -
remove the language selected in the list from the system. This button should be used
with caution, as every text item in this language will also be removed. Use the Disable button to temporarily disable a language but still retain
any text items.†
Properties -
change the properties of the selected language.††
Set Default -
Set the selected language as the default language. One of the languages must be
set as the default and it is displayed in a bold font. The significance of the
default language is that it becomes the default runtime language (see determining runtime language) and can also be used
in selecting text items to display to the user (see how
texts are selected for display).
Enable/Disable
Ė Enable or disable the selected language. This is a toggle switch with only
one of Enable or Disable being displayed. A disabled language is not available to
users.
Both the Add
and Properties buttons access the
properties dialog.†
 †††††
†††††
Language Code: this can only be entered when adding a new
language. Select from the dropdown list. See Language
Codes below.
Description: the description of the language used throughout
the system to represent the language.†
Enabled: specifies whether the language is enabled or disabled. A disabled
language is not available to users.
Format and Formatting language
This section provides the ability to change the
format used to present and enter numeric and date fields. When a new language
is added, the formatting language is
initially set to the same value as the Language Code, but a different
formatting language can be specified if required. For example, a French
division of an international company might require that all numeric and date
formatting be done using American conventions. In this case, the language code
could be set to 'fr', and the formatting language set to 'en_us'.
The format area below the formatting language is
display only and provides an example of how various field data will be
displayed to users.†††
Use default encoding: use the default encoding
provided by the application server for the language. You should only change
this if you think that the application server is not providing the correct
encoding.
Always use: directs the system to always use the specified
encoding for this language. If the encoding you require is not in the dropdown
list, it can be typed in.
Note that this specification of character encoding
for a specific language can be overridden. See Character Encoding tab.
Language Codes
Ebase uses RFC 3066 language identifiers.†† This language code is split into sub tags,
where a '_' character delimits each sub tag.††
Normally, the first sub tag represents a language from ISO 639. Second
or subsequent sub tags are optional, and further identify the language. Often
the second sub tag is a two character country code (ISO 3166).†† Full detail of this standard is available here.† ††
In this way, primary languages (such as French and
English) may be used several times, each time with different sub tags. For
example, the languages 'en' (English), 'en_gb' (British English) and† 'en_us' (American
English) may coexist.†
Ebase takes advantage of this language hierarchy
both when identifying the user's runtime language and when selecting the
language of a text item. So, for example, the user may be identified as
American (en_us) but, where a particular American text item does not exist, it
can be safely shown as an English (en) text item. This gives the Ebase user the
ability to handle subtle differences between similar languages with a minimum
of typing. This is explained further below.
Determining User Runtime Language
The user's runtime language is determined as each
form is started. The strategy for determining the userís language is defined
using the Options tab of the
internationalization dialog on the tools menu (Tools -> System Preferences ->
Internationalization).

The system uses the following three methods in turn
to determine the runtime language. If a method results in a language choice,
the language chosen is used; if not, the system moves to the next option. The
first two methods are configurable and can be enabled or disabled using the
checkbox to the left of each item.
1.
Use the URL
language parameter:† a language
code may be added to the URL used to invoke the form using parameter LANGUAGE. e.g.
the following URL www.myco.com/ufs/ufsmain?formid=MYFORM&LANGUAGE=FR will run the MYFORM form in French,
if French is a valid supported language. This is the technique used by the
Designer to submit a form in a specific language. This option can be enabled or
disabled using the checkbox to the left of the item, but note that disabling
the option will prevent testing of multiple languages from the Designer.†
2.
Try to honour the
users browser setting:†
the languages
that have been configured in the userís web browser are examined in turn. The
first language to match a supported language is used. This setting allows the
automatic setting of language to the userís preference as configured in the
browser he/she is using. This option can be enabled or disabled using the
checkbox to the left of the item.
3.
The system
default language:† if a language has not been
determined by one of the methods above, the system default language is used.
This option cannot be disabled.
The setting of runtime language lasts for the
duration of the userís session and will be carried through to subsequent forms
executed. When accessing subsequent forms, the LANGUAGE URL parameter may be used to override the current
language, however the browser setting and default language will be
ignored.††
It is also possible to change the runtime language
programmatically:
API
based languages:
form.language = "ES";
FPL:††
set $LANGUAGE = 'ES';
Where XXX evaluates to the language code of a supported language. If the language does not exist, an
error will occur.
†
How texts are selected for display
There are three Ebase elements that support multiple
language texts. These are:
∑
Texts:†††††††††† All form and system texts
∑
Messages:†††† All messages displayed to the user
∑
Static
Lists:††† All static list displayed texts.
(See How to use Static Lists for more
information)
Together these elements provide total support for
presenting a form in any number of languages.
As a form is displayed to a user, the most
appropriate text for each text item above is chosen according to the userís
runtime language as described by the following rules:
1. The system first checks if a text
exists for the language code of the userís
runtime language.
2. If not, the sub tags are removed from the language code one by
one until a match is found.††
3. If a text has still not been found,
the default language is used.††††
It is important that all text items are completed
for the default language, otherwise a form could be
displayed with missing texts.
Example:†††
A form has 5 text items: text item
1 -> 5, and there are three supported languages:† en (English), fr (French),
and fr_BE (Belgian French). The default
language is en.
The following table shows the texts that have been
configured using the Ebase Designer:
|
Text item |
text
for en |
text
for fr |
text
for fr_BE |
|
1 |
XXXX |
YYYY |
ZZZZ |
|
2 |
AAAA |
BBB |
|
|
3 |
PPP |
|
QQQ |
|
4 |
WWW |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
The following table shows the texts that are
displayed to the user when language fr_BE or fr is chosen as the runtime language:
|
Text item |
fr_BE |
fr |
|
1 |
ZZZZ |
YYYY |
|
2††††††††††††† |
BBB |
BBB |
|
3 |
QQQ |
PPP |
|
4 |
WWW |
WWW |
|
5 |
|
|
When fr_BE is the runtime language, the two texts configured for this language - text items 1 and 3 - are displayed (Rule 1). Text item 2 is displayed using language fr (Rule 2), and the remaining text items are taken from the default language en (Rule 3).
When fr is the runtime language, the two texts configured for this language - text items 1 and 2 - are displayed (Rule 1). The remaining text items are taken from the default language en (Rule 3).
†
Formatting of numeric and date fields
Integer, Numeric, Currency, Date and Datetime form
fields are formatted according to the user's languages setting. Values also
need to be entered using this format. See formatting language
above for details of these formats.††
The user's language can make significant differences
to the value of an input. For example: 123,233 in France means something
totally different to 123,233 in UK, where a comma is a decimal point character
in France and a digit group separator in the UK.†††
The presentation of dates also
vary according to language. For example: 10th April 1970 in the
The use of the digit group separator is
optional for input data received from the user. The display of digit group separators is also
optional and can be set on the presentation tab of the field properties dialog.
When disabled, a number is presented as a sequence of digits. e.g. value
1234567 is displayed with language English as:
|
With digit group separator: |
1,234,567 |
|
With no digit group separator: |
1234567 |
Setting Character Encoding
A character encoding is used to encode data
transmitted between the server and user browsers. In general, the Ebase system
requests the application server to set a character encoding based on the runtime
language. In most cases, this should result in the correct encoding. However,
it is possible to override this process and configure a specific encoding to be
used for each language, and it is also possible to specify a single encoding to
be used for all languages.
The character encoding can be configured using the Character Encoding tab of the
internationalization dialog on the tools menu (Tools -> System Preferences ->
Internationalization)
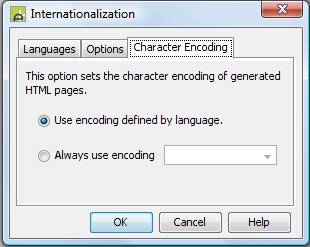
Use encoding defined by the language: this is the default setting. The encoding for each language can be separately configured in the language properties.
Always use encoding: directs
the system to always use the specified encoding for all languages regardless
of the character encoding setting configured for individual languages. If the
encoding you require is not in the dropdown list, it can be typed in.
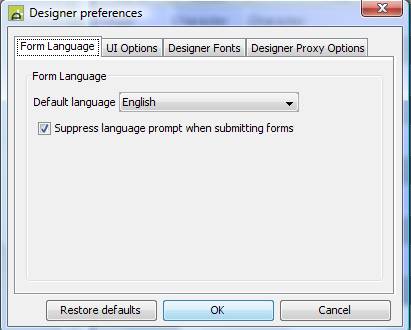
Ebase Designer Language Preference
The current Ebase Designer Language can be changed in the Ebase Designer Preferences dialog box on the file menu (File -> Preferences).†† Form texts will be displayed in this language when editing a form.† Please note that if no text is found for a text item, then a fall back language (i.e. en_us -> en -> default) will not be used.
†††