Working with CSV Resources
Creating a
CSV resource in Ebase Designer
Coding FPL script
commands to access the resource
See also:
Understanding Ebase Integration
What is a CSV
resource?
Ebase
provides a CSV resource to support the ability to create a .csv file containing
a comma delimited list of field values extracted from an Ebase form. A CSV
resource is a specific implementation of a custom resource. It allows form data
to be written to a csv file and is implemented by a Java class supplied with
the Ebase standard distribution. When a WRITE command is issued against a CSV
resource, a comma delimited record is written to the specified file. All the
fields of the form, except event fields and buttons, are included. The fields
are arranged in strict alphabetical field name order. Character fields are
enclosed in double quotes ("). Each " contained within a character
field is changed to a \". When required (when the 3rd parameter
is set to Y), a header record is also written, containing all field names
except event fields and buttons, again in strict alphabetical field name order.
The header record is written only when the file is first created. Subsequent
write requests will result in additional lines being added to the target file.
Please note
that a CSV resource differs from other external resources in that resource
fields are not required and mappings between form fields and resource fields
are similarly not required. Instead a CSV resource works directly on form
fields and will output all form field values contained in the form from which
it is invoked, with the exception of event fields and buttons.
The steps
involved in using a CSV resource are fundamentally same as the steps in using
other external resources:
1.
Create the resource as described below.
2.
Add the resource to a business view.
3.
Associate the business view with the form.
4.
Issue Write script commands against the resource
name.
Creating a CSV resource in Ebase Designer
The steps
involved in creating a CSV resource are the same as those for a custom
resource. What turns a custom resource into a CSV resource,
is the name of the implementing java class. Furthermore, three parameters are
required which must be set according to the requirements of the user of the
resource.
Open the
custom resource editor by either clicking on an existing custom resource in the
hierarchy tree panel (IT Elements -> External Resource -> Custom
Resource) or selecting (File -> New -> External Resource ->
Custom Resource)
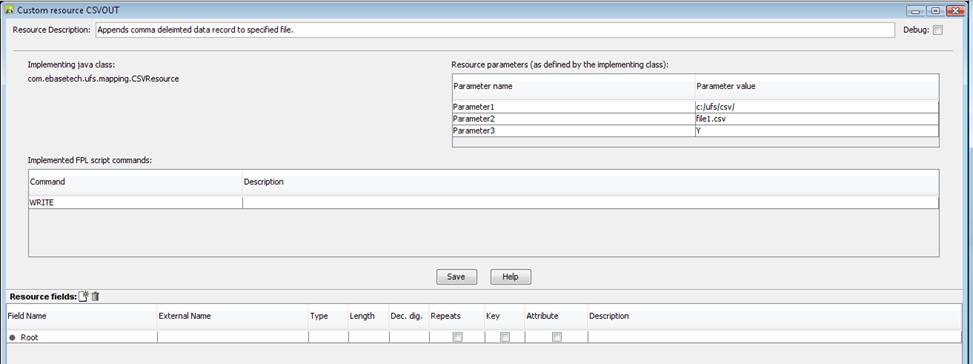
Resource
Description allows you to provide a description of this custom resource.
Implementing
Java class must specify com.ebasetech.ufs.mapping.CSVResource as
shown above.
Resource
parameters: There are three parameters of which the first two are
mandatory.
The first
parameter is a string representing a valid directory name(e.g.
D:/UFS/CSV/ ). The nominated file (next parameter) will be created or located
in this directory.
The second
parameter is a string representing a valid file name. This file will be created
if it does not already exist. If it already exists, data will be appended to
the end of the file.
The third
parameter is optional. When set to Y (not case sensitive), a header record will
be written to the file when the file is first created. Subsequent WRITEs will
not write a header record.
Implemented script commands: Only the write command is implemented by this resource.
Resource fields are not required for a CSV resource
and will be ignored if created. A write command to A CSV resource will always
output all form fields with the exception of event fields and buttons.
Coding FPL script commands to access the resource
Issue the write
command e.g.
|
FPL: |
API based language: |
|
write CSVOUT; |
resources.CSVOUT.write(); |