Working with Sequences
Creating
and editing a sequence
Sequences
and transactionality
See also:
Understanding Ebase Integration
What is a sequence?
A sequence
is used to supply the next number from a defined sequence. It is designed to be
used when you are building a form to create some form of new document, e.g. an application
form. The sequence can be used to give each application a unique sequential id.
Sequences are stored in the Ebase repository database.
Once a
sequence has been created, it can be used by any number of forms.
How to use a sequence
The sequence
is used via the sequence FPL script command which sets the
$NEXT_SEQUENCE_ID system variable. For example, to create a new unique id for
an application form, we would use the following FPL commands:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
sequence APPLICATIONS; set APPLICATION_ID = $NEXT_SEQUENCE_ID; |
var next = system.sequenceManager.sequence("APPLICATIONS"); fields.APPLICATION_ID.value
= next; |
where
APPLICATIONS is the name of the sequence and APPLICATION_ID is the form field
for the unique id.
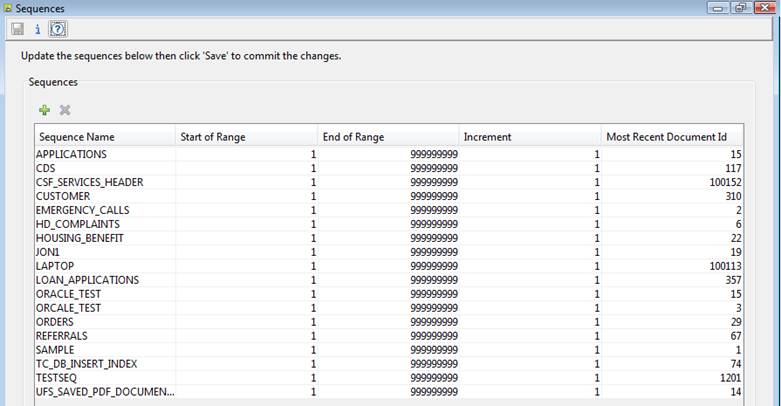
Creating and editing a sequence
Sequences are created and maintained by
clicking in the hierarchy tree panel (IT Elements -> Sequences).
·
Sequence name is name by which the
sequence is referenced in the sequence FPL command or API SequenceManager.sequence() method.
·
Start of range is the lowest number
within the sequence.
·
End of range is the highest possible
number within the sequence. When this number is reached, the sequence command
will fail and the form will be terminated.
·
Increment is the number by which the next
document id should be incremented each time a new sequence is assigned.
·
Next document id is the number to be used
when the sequence is next accessed.
Click the ![]() icon to add a new sequence and the
icon to add a new sequence and the ![]() icon to delete selected sequences.
icon to delete selected sequences.
Sequences and transactionality
Sequences are incremented using a separate transaction from the main Ebase form execution. When the sequence FPL command or API SequenceManager.sequence() method is issued, a new sequence number is immediately assigned and the Ebase sequences database table is updated. If there is a subsequent failure in a script, the sequence will not be rolled back. It is therefore possible that there will be gaps in the sequence of documents created using a sequence.
See also Understanding Ebase events and Transaction Support.
Importing/exporting
sequences
When sequences are selected for
export, all sequence definitions are
exported; it is not possible to export single definitions. Similarly an import
will replace all sequence definitions and will also import the Most recent Document id, which could
potentially compromise data integrity on the importing system. For these
reasons, sequences are not automatically included in an export file when a form
is exported with all related elements.
Sequence definitions should be
created manually on the import target system.