Working with Stored Procedures
What
is a stored procedure resource?
Creating
and editing stored procedure resources
Stored Procedure Resource Toolbar
FPL
script command to invoke a stored procedure
Supported
database column types
SQL
Server Stored Procedures Support
See also: Understanding
Ebase Integration
This document describes how to use Ebase Stored Procedure
Resources to call stored procedures and functions defined in a database. Ebase
provides support for all the various types of parameters used as input and
output including: IN parameters, OUT parameters, INOUT parameters,
RETURN parameter, QUERY parameters. Please note that Ebase does not currently
provide support for stored procedures that return multiple result sets.
To access
stored procedures and functions with overloaded parameter definitions, it is
necessary to create one Ebase Stored Procedure Resource for each combination
supported by the DBMS. In addition, Ebase requires that each resource has a
unique name. Overloading could be implemented as shown in the following
example:
Database
Ebase
|
PROC1(A,
B, C) |
PROC1_A |
invokes PROC1
with parameters A, B, C |
|
PROC1(A,
B, C, D) |
PROC1_B |
invokes
PROC1 with parameters A, B, C, D |
What is a Stored Procedure Resource?
A Stored
Procedure Resource represents a call to a single database stored procedure or
function. When creating a Stored Procedure Resource you need to specify the
name of the stored procedure or function in the database and the name and type
of all input and output parameters. These parameters are then mapped to form
fields in the same way as for all other Ebase resources.
A stored
procedure is invoked with the FPL exec command
or API StoredProcedureResource.exec() method. These statements are used for
all calls to a stored procedure regardless of the function performed by the
stored procedure.
To use a
Stored Procedure Resource in a form, it is necessary to go through the
following steps.
1.
Configure the connection to the database.
2.
Create the Stored Procedure Resource.
3.
Add the resource to a business view.
4.
Associate the business view with the form.
5.
Map the form fields to the resource fields i.e.
the stored procedure parameters.
Steps 1, 3,
4, 5 are described in Database Resources.
This documentation describes only those processes that are unique to stored
procedures.
Stored
procedure resources are sharable elements within the Ebase system and, once
created, can be used by any number of forms.
Creating and editing Stored Procedure Resources
Open the Stored Procedure
Resource editor by either clicking on an existing Stored Procedure Resource in
the hierarchy tree panel (IT Elements -> External Resource -> Stored
Procedure Resources) or selecting (File -> New -> External
Resource -> Stored Procedure Resource). The following example shows an
existing Stored Procedure Resource named FIND_APPROVER that has 4 IN parameters
and 5 OUT parameters. This has been imported directly from an Oracle database
with the result that the length and decimal digits fields have not been set, as
these are not available to the DBMS system.
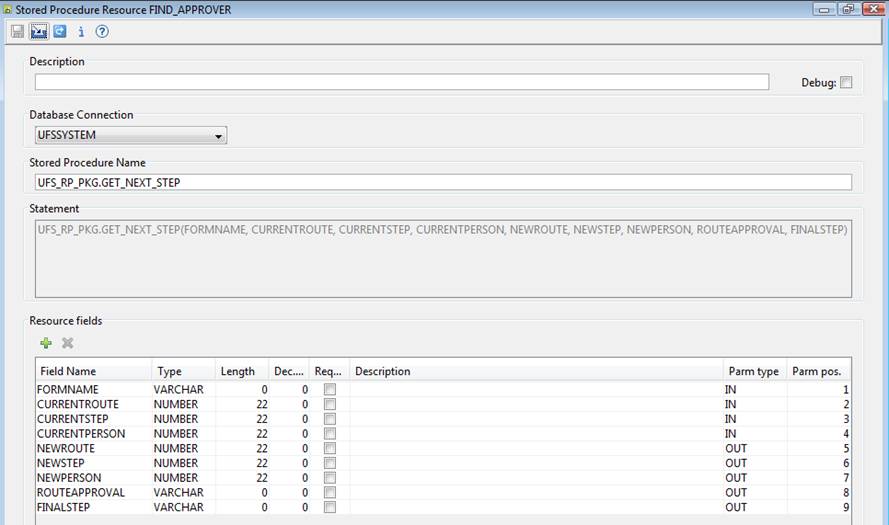
·
The Database Connection dropdown list
specifies the database connection to be used and contains a list of all defined
Database Connections to which the Ebase
system has access. The special entry **Dynamic can be chosen to indicate
that the database name will be supplied dynamically at runtime.
·
The stored procedure name field is the
name of the stored procedure or function in the database.
·
The statement field is read only and is
provided to show the format of the call statement that Ebase builds to invoke
the stored procedure.
·
The resource fields table contains all
the parameters used by the stored procedure.
·
Field name must match the name of the
parameter within the stored procedure or function.
·
The field type should be set to match the
database parameter type. The values available in the dropdown are the types
from the JDBC standard. See your database documentation for how these map to
your database types. The system makes use of these types when converting the
value received from the database to the mapped field within the form. If an
illegal mapping is detected, you will receive an error message.
·
The length and decimal digits are
only used by Ebase when resource fields are imported into a form, and then they
set the corresponding length and decimal digit specifications for a form field.
·
Required should be checked for IN
parameters that must have a value. If required is checked and no value
exists, a runtime error message is generated. If required is not checked
and the field has no value, a null is passed to the DBMS.
·
The field description can be used to
enter meaningful information about the field. This information is visible to the
Ebase user when building the form field mappings.
- Parameter
type must match the corresponding type of the stored procedure or
function parameter. The following values are available from the dropdown
list displayed by clicking on the field:
|
IN |
IN parameter |
|
OUT |
OUT parameter |
|
INOUT |
INOUT parameter |
|
RETURN |
The single RETURN parameter from a function |
|
QUERY |
Result set query parameter made available by the stored procedure or function |
- Parameter
position. All parameters except QUERY parameters must be numbered in
the same sequence as they appear in the stored procedure or function in
the database. If a RETURN parameter exists it must be number 1. All other
parameters should be numbered sequentially.
Stored
Procedure Resource Toolbar
![]()
![]() Save: saves the Stored Procedure Resource.
Save: saves the Stored Procedure Resource.
![]() Runs the database schema wizard to import a stored
procedure directly from the database. This has the advantage that all
parameter names and types will be correctly set. Please note that different
database systems vary in behaviour and implementation of stored procedures and
functions, and that the data imported can also vary, e.g. parameter lengths may
not be available.
Runs the database schema wizard to import a stored
procedure directly from the database. This has the advantage that all
parameter names and types will be correctly set. Please note that different
database systems vary in behaviour and implementation of stored procedures and
functions, and that the data imported can also vary, e.g. parameter lengths may
not be available.
![]() Add the resource to one or more Business Views. Supports
both adding to one or more existing Business Views and the creation of a new
Business View. Existing Business Views can only be changed when they are
not already open.
Add the resource to one or more Business Views. Supports
both adding to one or more existing Business Views and the creation of a new
Business View. Existing Business Views can only be changed when they are
not already open.
![]() Show information: shows userid and dates for
creation, last update and import of this Stored Procedure Resource.
Show information: shows userid and dates for
creation, last update and import of this Stored Procedure Resource.
![]() Shows this help page.
Shows this help page.
FPL script command to invoke a
stored procedure
The EXEC script command is used to invoke a stored procedure
resource. e.g.
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
exec CLIENT_CHECK; See FPL Script Command
Syntax for more information. |
resources.CLIENT_CHECK.exec(); |
Supported
database column types
All database column types are supported with the exception
of the following: all binary types, e.g. BIT, BINARY, LONGBINARY, IMAGE etc,
plus CLOB, BLOB, REF, STRUCT, JAVA_OBJECT.
SQL Server Stored Procedures
Support
Microsoft SQL Server allows you to write a stored procedure
with spaces in the name, e.g. ‘update MyTable’. To support invoking stored
procedures with spaces in the name using the Ebase stored procedure resource
dialog, wrap the stored procedure name with ‘[‘ and
‘]’,
Add [ and ] to the beginning and
end of the stored procedure name textfield:
[update MyTable]
Wrapping the name using [ and ] is standard syntax
recognized by SQL Server when exec a stored procedure with spaces in the name,
e.g. exec [Update MyTable] ‘data1’, ‘data2’ etc..