Working with MQ Series
Adding
the resource to a business view
Associating
the business view with a form
Mapping
resource fields to form fields
Reading
and writing MQ Messages
See also: Understanding Ebase Integration, Using the XML JMS Adapter
Configure the MQ system
Before you can send MQ messages from an Ebase form, you must
first configure the target MQ server. This is done with parameters Ufs.mqHostId
and Ufs.mqPort of the Ebase startup parameters.
What is an MQ resource?
Each MQ
resource represents a single MQ message to be read or written. When a message
is written, an option exists to support waiting for a response and then reading
this response. Ebase Xi allows you to substitute values from the form at
runtime into any of the MQ parameters: text, sender, recipients etc.
Each MQ
resource contains two sections: the MQ message section where you
configure the destination of the MQ message and optionally the source of the
expected reply message, and a Resource
fields section which contains a list of substitutable fields. These
fields are mapped to the form fields to enable the system to perform the
dynamic runtime substitution of values. When using MQ formats MQSTR or MQRFH2
(used for JMS messages), a single field is used to represent the message data.
MQ resources
are sharable elements within the Ebase system and, once created, can be used by
any number of forms.
Creating an MQ resource
Open the MQ resource editor by either
clicking on an existing MQ resource in the hierarchy tree panel (IT Elements
-> External Resource -> MQ Resources) or from the file menu (File
-> New -> External Resource -> MQ Resource). The following example
shows an existing MQ resource.
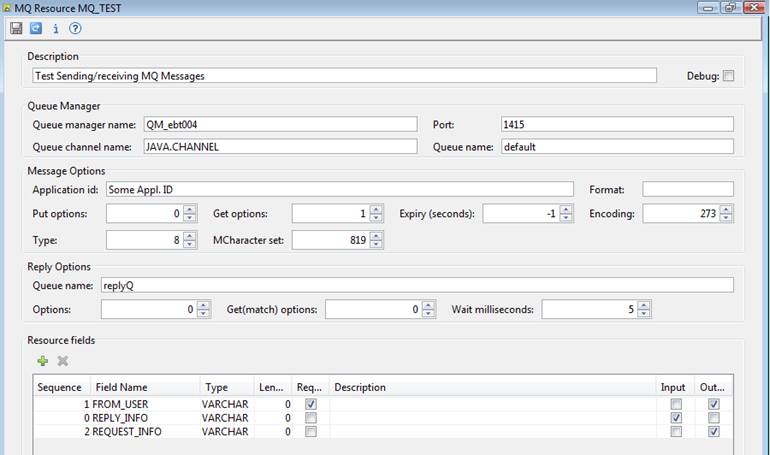
Description
allows you to provide a description of this MQ message.
Debug: additional messages are written to the execution log.
The
remaining fields are standard MQ configuration parameters and control the
manner in which a message travels between sending and receiving applications.
Queue manager name is required and should be a valid queue manager on the MQ server.
Port: specifies the MQ listener port.
If not specified, the value for property Ufs.mqPort in Ebase startup parameters is used. If this
property is not specified, the default MQ listener port is used.
Queue
channel name is required and should be a valid channel for the specified
queue manager on the MQ server.
Queue
name is required and should be a valid channel for the specified queue
manager on the MQ server.
Put
options, Get options, Message expiry seconds, Message encoding, Message type
and Message character set are all required and are numeric.
Message
application Id. and Message format are optional. When the message
format is MQSTR, the message is treated as a single string variable that is
read or written using a single field. See MQ
format MQSTR. Message format MQRFH2
should be used to read and write JMS messages. See MQ
format MQRFH2.
Reply
Queue name, Reply options, Reply Get(match) options and
Reply wait milliseconds are applicable only when the WAIT clause
accompanies a write MQ_resource_name
command.
Resource Fields
The lower
section is the Resource fields
section. You must create one field definition for each field that you want to
map to a form.
Type
determines the treatment of the value at send/receive time. Length is
relevant to Type CHAR only and signifies a fixed length field. When
sending a fixed length message, the field data is truncated or padded with
spaces to the specified length. When receiving a message, the system will read
a string of the specified length.
If the Required
checkbox is ticked, a write script
command to send the MQ Message will fail unless a value exists for the mapped
field.
A field
will be included in an outgoing MQ Message, only if the Output checkbox
is ticked.
If any Input checkboxes are ticked and a reply message is
expected, as many fields as necessary will be read from the reply message and
their values stored in the Input fields.
Output fields are shown first, followed by Input fields. Sequence determines the ordering within each group, both within Ebase Designer and at message composition/decomposition time.
Resource fields toolbar
![]()
![]() Add a resource field
Add a resource field
![]() Delete selected resource fields
Delete selected resource fields
MQ
Resource toolbar
![]()
![]() Save: saves the MQ resource.
Save: saves the MQ resource.
![]() Add the resource to one or more Business Views. Supports
both adding to one or more existing Business Views and the creation of a new
Business View. Existing Business Views can only be changed when they are
not already open.
Add the resource to one or more Business Views. Supports
both adding to one or more existing Business Views and the creation of a new
Business View. Existing Business Views can only be changed when they are
not already open.
![]() Show information: shows userid and dates for
creation, last update and import of this MQ resource.
Show information: shows userid and dates for
creation, last update and import of this MQ resource.
![]() Shows this help page.
Shows this help page.
Using an MQ Resource
Adding the resource to a business view
Click the ![]() icon on the toolbar.
icon on the toolbar.
Associating the business view with a form
In the form editor, select the business view from the
dropdown list in form properties.
Mapping resource fields to form fields
To create mappings automatically
between form fields and a resource fields, simply import the resource fields
into the form using the Import fields from external resource icon on the
Fields
View toolbar of the form editor.
This will create new form fields of the appropriate type and length and will
also create the mapping.
To create mappings manually,
click on the field mappings icon on the form toolbar of the form
editor, select the resource to be mapped, then select
the form fields for each of the resource fields from the dropdown list.
Reading and writing MQ Messages
MQ resources support both READ and WRITE commands:
Read command:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
read MQ_resource_name; |
resources.MQ_resource_name.read(); |
Reads a message and extracts individual field values. Field values are extracted by parsing the message from left to right and extracting all fields flagged as input fields in the order specified by the field sequence. CHAR fields are treated as fixed length and the number of characters read is specified by the field’s length; VARCHAR fields have a variable length and are preceded by a length header in the message – the length specified for the field is not used.
Write command:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
write MQ_resource_name; write MQ_resource_name WAIT; |
resources.MQ_resource_name.write(); // write with WAIT resources.MQ_resource_name.write(true); |
Constructs a message from individual field values and writes the message. If WAIT is specified, waits for a reply to arrive on the reply queue message and then issues a read command to this queue. The output message is constructed from all fields flagged as output fields in the order specified by the field sequence. CHAR fields are treated as fixed length and the number of characters written is specified by the field’s length; if the field value is less than the field’s length, the data written is right padded with space characters; VARCHAR fields have a variable length and are preceded by a length header in the message.
MQ Format
MQSTR
This section of the documentation describes how to configure an MQ resource to create or read a message that just consists of a single string i.e. message format MQSTR. When this message format is specified, a single field is used from which the message is read or written. For READ operations, the system expects a single VARCHAR resource field to be configured with the Input checkbox ticked. For WRITE operations, the system expects a single VARCHAR resource field to be configured with the Output checkbox ticked. The example below shows a resource with two fields MESSAGE_IN and MESSAGE_OUT that can be used for both READ and WRITE operations.
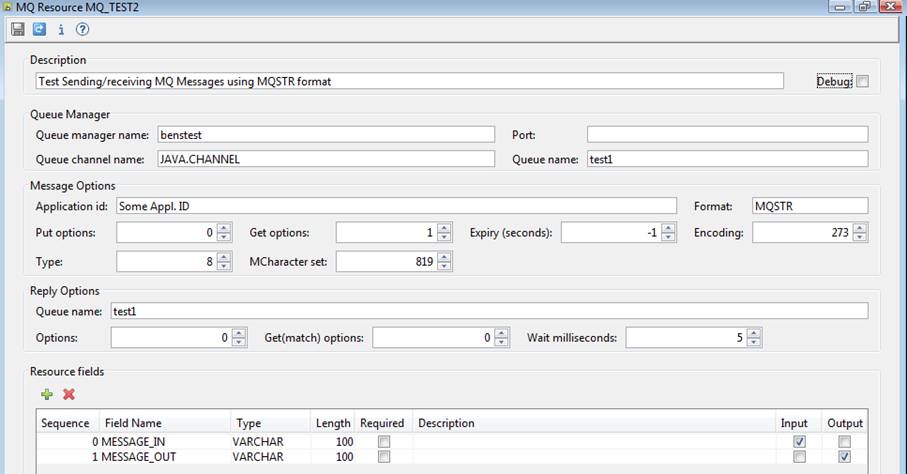
Note that Message format must specify MQSTR.
MQ Format
MQRFH2
Format MQRFH2 should be used to read a message created using JMS, or to create a message that is to be read using JMS. Messages with this format consist of a variable length header followed by the message payload. For read operations, the system ignores the header portion of the message except that the encoding and character set specified in the header are used instead of the corresponding values in the resource; it is not possible to access any name/value data contained in the header. For write operations, Ebase creates a minimal header without name/value data, and encoding and character set are taken from the resource.
When this message format is specified, a single field is used from which the message is read or written. For READ operations, the system expects a single VARCHAR resource field to be configured with the Input checkbox ticked. For WRITE operations, the system expects a single VARCHAR resource field to be configured with the Output checkbox ticked. The single field contains the message payload for both read and write operations. The example below shows a resource with two fields MESSAGE_IN and MESSAGE_OUT that can be used for both READ and WRITE operations.
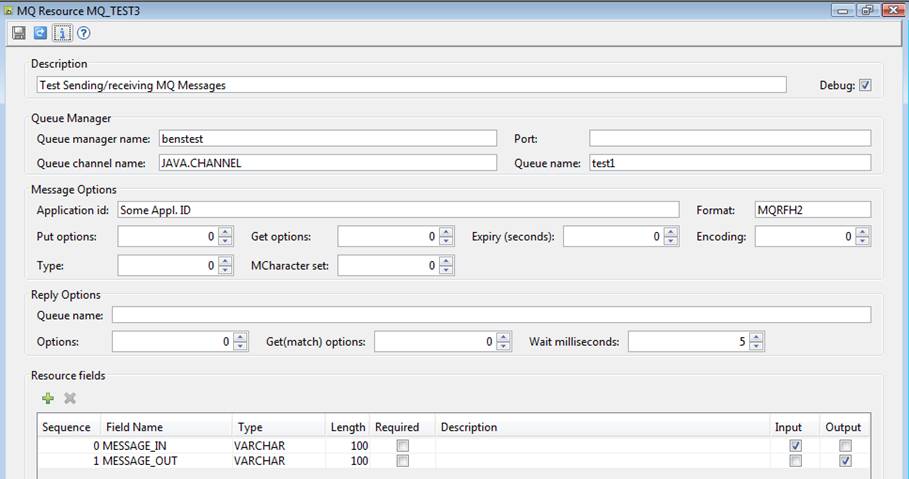
Note that Message format must specify MQRFH2.